Metabolism
How organisms acquire and process food for energy.
Metabolism & Energy Flow
energy transfer between organisms
Biology 2e (6.1)
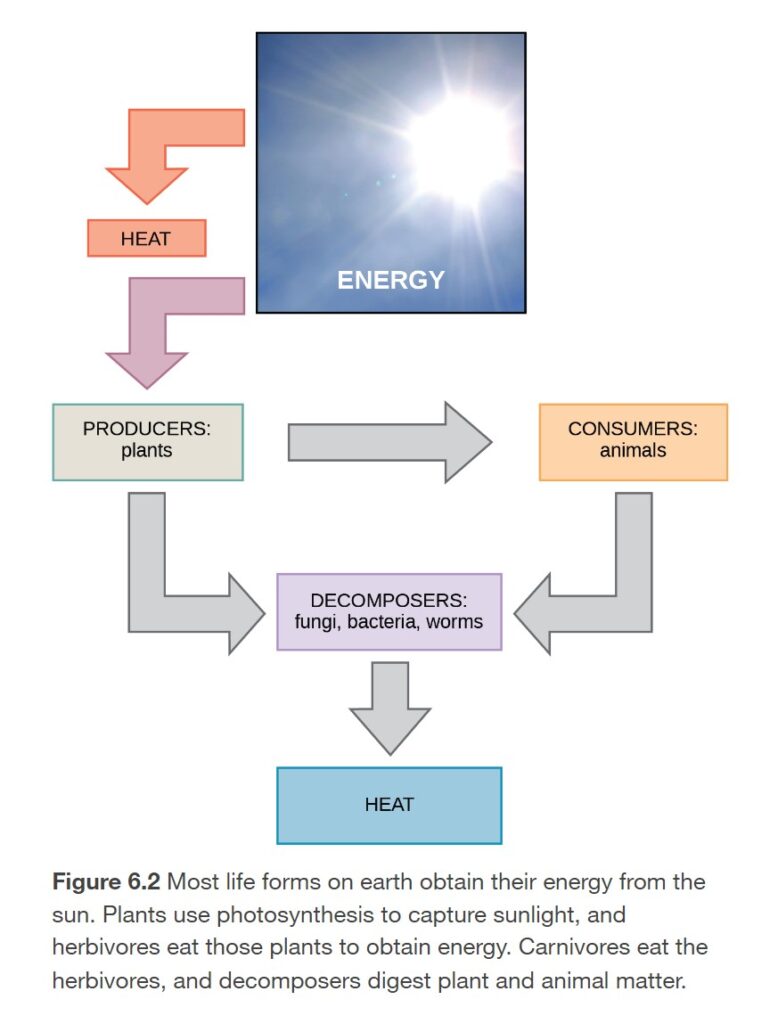
Energy flows between organisms according to the chart to the left. Primary produces, like plants, create their own food from sunlight in a process known as photosynthesis (we will explore this process later in the lesson). Consumers eat these producers and other consumers in order to obtain energy. When organisms die, decomposers break down the organic material and heat energy is released. Energy continues to cycle in this process.
Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions that transpire inside cells, both those that use or release energy. Anabolic process assemble small molecules into larger ones; these processes require energy. On the other hand, catabolic processes release energy. In these processes, a large molecule is broken down into smaller ones.
Metabolic Processes
obtaining energy to function
Cellular Respiration
In cellular respiration (carbohydrate metabolism) carbohydrates or sugars are broken down into a usable energy form, known as ATP. Because energy is released in this process, cellular respiration is a catabolic reaction.
The energy created during cellular respiration is then used by organisms to maintain metabolic functioning.
Photosynthesis
energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
In photosynthesis (a process used by primary producers) energy from sunlight is used to convert carbon dioxide into sugar molecules. Energy is required in photosynthesis, so this process is anabolic.
The sugar produced in photosynthesis is used my producers to supplement normal processes. When consumers eats producers, they obtain sugars (like glucose) that can be used to complete cellular respiration in order to produce energy. The cycle continues!
